As we embark on the journey into 2024, the global economic outlook or landscape is poised at a crossroads, balancing between recovery from the disruptions wrought by the COVID-19 pandemic and the pursuit of sustainable growth amidst evolving global dynamics.
Why We Need To Know Global Economic Outlook?
Understanding the global economic outlook is important for several reasons:
- Informed Decision-Making: Individuals, businesses, investors, and policymakers rely on economic forecasts to make informed decisions. By understanding the economic outlook, they can better anticipate trends, risks, and opportunities, guiding their actions regarding investments, hiring, spending, and policy formulation.
- Risk Management: Awareness of economic conditions helps in assessing and mitigating risks. Businesses can adjust their strategies to navigate economic fluctuations, while investors can diversify their portfolios to hedge against downturns or capitalize on growth opportunities.
- Policy Formulation: Governments and central banks use economic forecasts to formulate monetary, fiscal, and regulatory policies. By understanding the economic outlook, policymakers can implement measures aimed at stabilizing the economy, controlling inflation, promoting growth, and addressing societal challenges.
- Market Dynamics: Economic conditions influence market dynamics, including stock prices, interest rates, currency values, and commodity prices. Investors and traders closely monitor economic indicators to make decisions in financial markets.
- Long-Term Planning: Businesses and governments use economic forecasts for long-term planning. Understanding future economic trends helps in setting strategic goals, allocating resources, and preparing for potential challenges or opportunities.
Economic Outlook 2024
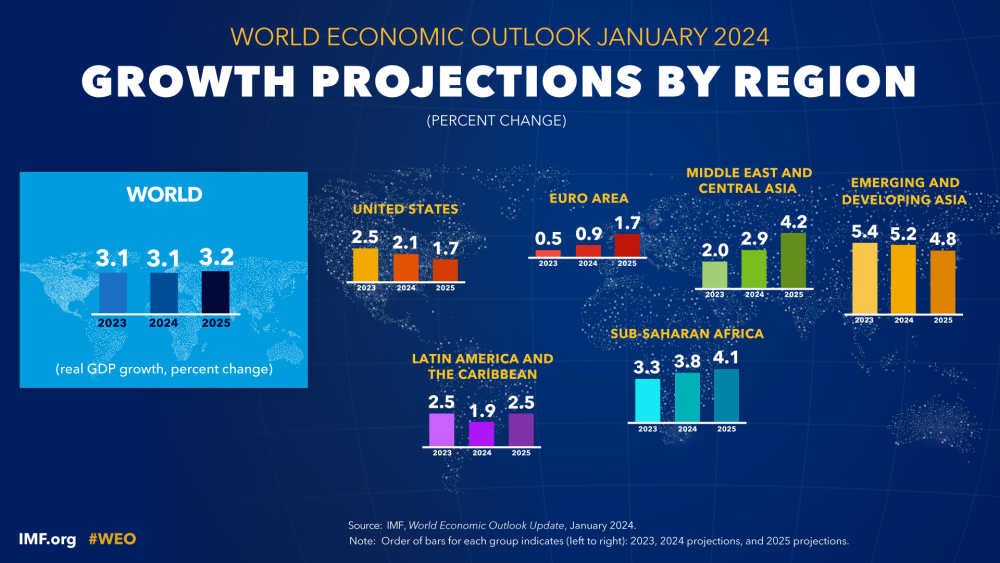
Based on the International Monetary Fund (IMF) released their forecasts in January 2024 about the global economic outlook 2024 segmented into the regions.
IMF makes a global growth projection based on the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of 3.1 percent in 2024, and 3.2 percent in 2025.
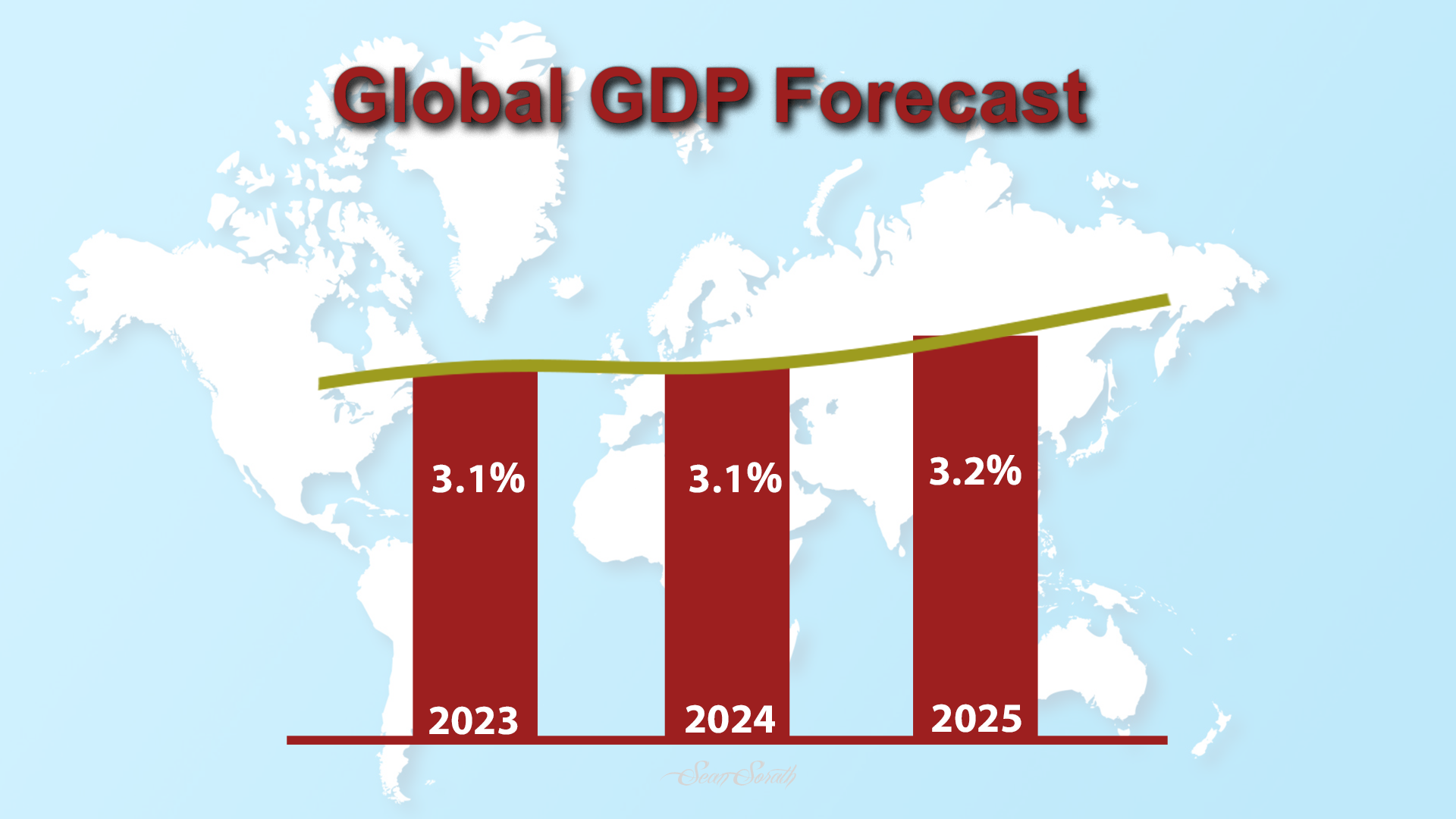
The projection also included the advanced economic countries’ growth of 1.5 percent in 2024 and 1.8 percent in 2025 and emerging countries’ growth up to 4.1 percent in 2024 and 4.2 percent in 2025
Below is the global economic outlook for 2024 by region developed by the IMF.
European Union Member Countries
IMF shows that European Union Countries’ growth rate is 0.5 percent and 0.9 percent in 2023 and 2025 accordingly whereas in 2025 the growth reaches up to 1.7 percent.
Below is some key information we need to know for the EU:
- Recovery from Pandemic: European countries were at various stages of recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic. While vaccination campaigns were underway, there were concerns about the emergence of new variants and the potential impact on economic reopening efforts.
- Inflation and Monetary Policy: The European Central Bank (ECB) continued its accommodative monetary policy stance to support economic recovery. Inflationary pressures were monitored closely, with debates over the transitory nature of inflation versus persistent factors.
- Green Transition: Europe continued to focus on its green transition agenda, with significant investments in renewable energy, sustainable infrastructure, and initiatives to achieve carbon neutrality. The European Green Deal remained a central policy priority.
- Trade Relations: Trade relations with the UK post-Brexit and ongoing trade tensions with the US and China influenced Europe’s economic outlook. Efforts to strengthen intra-European trade and diversify trade partnerships were observed.
United States of America (USA)
The USA has the most purchasing power in the world, this factor boosts its growth faster than other countries, but IMF forecasts the USA’s growth and economic outlook drop from 2.1 percent in 2024 to 1.7 percent in 2025.
The key information we need to know for the USA are:
- Post-Pandemic Recovery: The United States was in the midst of an economic recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic. Fiscal stimulus measures, vaccination campaigns, and gradual reopening of the economy supported growth, although disparities persisted across sectors and regions.
- Inflationary Pressures: Inflation emerged as a concern, driven by factors, such as supply chain disruptions, labor market dynamics, and expansive fiscal policies. The Federal Reserve closely monitored inflation trends and debated the timing and pace of policy normalization.
- Infrastructure Investment: The Biden administration’s focus on infrastructure investment aimed to stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and address long-standing infrastructure challenges. Discussions over infrastructure spending and funding mechanisms shaped the economic outlook.
- Trade Policy: Trade policy under the new administration influenced economic dynamics, including negotiations with China, renegotiation of trade agreements, and efforts to promote domestic manufacturing and exports.
Latin America And The Caribbean
Latin America and The Caribbean were projected to be more downtrend to 1.9 percent in 2024 and 2.5 percent in 2025.
We offer some general considerations and factors that typically influence economic forecasts for the region:
- Macroeconomic Environment: The economic performance of Latin American and Caribbean countries is often influenced by global economic conditions, including trends in major economies such as the United States, China, and Europe.
- Commodity Prices: Many countries in the region are major exporters of commodities such as oil, minerals, and agricultural products. Therefore, fluctuations in commodity prices can have a significant impact on their economic outlook.
- Political Stability: Political stability and government policies play a crucial role in shaping economic prospects. Stable political environments tend to foster investor confidence and support economic growth.
- Trade Relations: Trade agreements and relationships with other countries, particularly major trading partners, can affect export opportunities and economic growth prospects.
- Debt Levels: High levels of public debt can constrain government spending and investment, impacting economic growth. Monitoring debt sustainability is essential for long-term economic stability.
- Infrastructure Investment: Investment in infrastructure projects can stimulate economic activity and improve long-term growth prospects by enhancing productivity and connectivity.
- Social Factors: Socioeconomic indicators such as income inequality, poverty rates, and access to education and healthcare can influence economic performance and development outcomes.
Asia
Emerging and developing countries, in Asia have growth rates as high as 5.2 percent in 2024 and 4.8 percent in 2025 because the growth remains a large gap, especially for emerging countries.
The key indicators you need to know about Asia
- Diverse Recovery: Asian countries experienced diverse economic recoveries from the pandemic, reflecting variations in vaccination rates, containment measures, and exposure to global trade. Some countries, particularly in East Asia, showed resilience, while others faced ongoing challenges.
- Supply Chain Dynamics: Asia played a critical role in global supply chains, and disruptions highlighted vulnerabilities. Efforts to diversify supply chains, enhance resilience, and promote regional integration were observed.
- Technology and Innovation: Asia continued to drive technological innovation and digital transformation, with investments in areas such as artificial intelligence, fintech, and e-commerce. Digitalization accelerated across sectors, shaping economic growth prospects.
- Key Geopolitical tensions, including US-China relations, territorial disputes, and regional security concerns, influenced economic outlooks in Asia. Efforts to strengthen regional cooperation and mitigate risks were observed.
Middle East And Central Asia
This region is in good prospect growth, according to the IMF projection of the economic outlook, the Middle East and Central Asia growth rate is 2.9 percent in 2024 and 4.2 percent in 2025.
We will give you some general considerations and factors that typically influence economic forecasts for this region:
- Oil Prices and Production: Many countries in the Middle East are major oil exporters, and their economies are heavily reliant on oil revenues. Therefore, fluctuations in oil prices and production levels can significantly impact economic growth and government revenues in the region.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The Middle East and Central Asia region often experiences geopolitical tensions and conflicts, which can disrupt economic activity, deter investment, and lead to uncertainty.
- Diversification Efforts: Several countries in the region have been implementing economic diversification strategies to reduce their dependence on oil and gas revenues and promote non-oil sectors such as tourism, manufacturing, and technology.
- Infrastructure Investment: Infrastructure development is a priority in many countries across the region to support economic growth, improve connectivity, and attract foreign investment.
- Trade Relations: Trade relations and agreements with other countries, as well as regional economic integration efforts, can influence economic prospects and trade flows.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks in the region implement monetary policies to manage inflation, support economic growth, and maintain currency stability.
- Labor Market Dynamics: Demographic trends, youth unemployment, and labor market reforms can affect economic performance and social stability in the region.
Sub-SAHARA Africa
IMF also projected growth in Sub-Saharan Africa for 2024 and 2025 of 3.8 percent and 4.1 percent respectively of their global economic outlook in 2024.
Below we offer some general considerations and factors that typically influence economic forecasts for the region:
- Commodity Prices: Many countries in Sub-Saharan Africa rely heavily on exports of commodities such as oil, minerals, and agricultural products. Therefore, fluctuations in commodity prices can have a significant impact on economic growth and government revenues in the region.
- Infrastructure Development: Investment in infrastructure is crucial for economic development in Sub-Saharan Africa. Improvements in transportation, energy, and telecommunications infrastructure can enhance productivity, facilitate trade, and attract investment.
- Demographic Trends: Sub-Saharan Africa has a young and rapidly growing population. While this presents opportunities for economic growth, it also poses challenges related to unemployment, education, and healthcare.
- Political Stability: Political stability and governance play a critical role in shaping the economic outlook or prospects in the region. Stable political environments can attract investment and support economic growth, while political unrest and conflict can hinder development.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): FDI inflows can contribute to economic outlook or growth by providing capital, technology, and expertise. Factors such as regulatory environment, infrastructure quality, and political stability influence the attractiveness of Sub-Saharan African countries to foreign investors.
- Trade Relations: Trade relations with other regions, including China, Europe, and the United States, impact economic growth and diversification efforts in Sub-Saharan Africa. Regional economic integration initiatives also play a role in promoting trade and investment within the continent.
- Debt Sustainability: High levels of public debt can constrain government spending and investment in Sub-Saharan Africa. Monitoring debt sustainability and implementing prudent fiscal policies are essential for long-term economic stability.
If you have any questions or doubts, please drop your comments In the below comment box – Thanks


